What Is an Electrostatic Precipitator and How Does It Work in Industrial Air Pollution Control?
 By Admin
By Admin
Introduction
In today’s industrial landscape, air pollution control is a critical concern for manufacturing plants, power stations, chemical processing facilities, and a wide range of other industries. Industrial emissions, including flue gases, fumes, and dust particles, pose significant risks to both human health and the environment. To address these concerns, technologies like the electrostatic precipitator (ESP) have become indispensable in reducing airborne particulate matter.
What is an Electrostatic Precipitator?
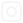
An electrostatic precipitator (ESP) is a highly efficient device used to remove suspended particulate matter from industrial exhaust gases. The ESP works on the principle of electrostatic attraction, where airborne particles are charged and then collected on a grounded surface, removing them from the air. The device typically consists of two key components: a discharge electrode and a collector electrode. When high-voltage direct current (DC) is applied to the discharge electrode, a strong electric field is generated. This field ionizes the particles in the air, causing them to acquire a negative charge. The negatively charged particles are then attracted to the positively grounded collector, where they are accumulated and eventually removed through a combination of vibration and mechanical methods.
How Electrostatic Precipitators Work
The basic operation of an electrostatic precipitator can be broken down into several steps:
Ionization of Particles: As flue gas or exhaust air enters the precipitator, the discharge electrode generates a high-voltage electric field. This field ionizes the suspended particles, giving them a negative charge.
Attraction to Collector: The negatively charged particles are then drawn to the positively charged collector electrodes due to the attractive forces between opposite charges.
Collection and Disposal: The collected dust particles accumulate on the collector plates. These plates are periodically cleaned through vibration or ultrasonic techniques, ensuring that the dust is removed and collected in an ash hopper at the bottom of the ESP.
Exhaust Air Treatment: The clean air, now free from dust and particulate matter, is safely released back into the environment.
Advantages of Electrostatic Precipitators
Electrostatic precipitators are widely considered one of the most efficient technologies for air pollution control. Here are some key advantages of using ESPs in industrial settings:
High Efficiency: ESPs can remove up to 99% of particulate matter, including fine dust and fume particles, making them highly effective for fume mitigation.
Low Maintenance: Compared to other filtration systems, ESPs require relatively little maintenance. The vibration or ultrasonic cleaning system ensures that the collector plates remain clear of dust, reducing operational downtime.
Energy Efficiency: ESPs are energy-efficient due to their use of high-voltage direct current (DC) rather than more energy-intensive methods like wet scrubbing or mechanical filtration.
Minimal Operational Costs: The electrostatic precipitator’s relatively simple design and operation translate to low operational costs over the long term.
Scalability: ESPs can be easily scaled to accommodate large industrial operations or smaller facilities, making them a versatile solution for various applications.
Industrial Applications of Electrostatic Precipitators
Electrostatic precipitators are used in various industries to treat exhaust air and mitigate fumes from industrial processes. Some common applications include:
Metallurgy Industry
The metallurgy industry, which involves the extraction and processing of metals from ores, generates large amounts of dust, smoke, and other particulate matter. ESPs are extensively used to capture these particles, particularly in processes like smelting and refining, where high-temperature operations release hazardous fumes and fine particulate matter. By using electrostatic precipitation, the industry can significantly reduce the emission of pollutants, protecting both workers and the environment.
Cement Manufacturing
The cement industry produces significant amounts of dust and particulate matter during the production process. ESPs are used to capture these particles, preventing environmental contamination and ensuring cleaner air in cement plants.
Steel Manufacturing
Steel mills produce fine particulate emissions due to high temperatures and chemical reactions involved in steel production. Electrostatic precipitators effectively remove these particles, improving air quality and reducing health risks for workers.
Chemical and Petrochemical Plants
Chemical plants and refineries often generate flue gases rich in particulate matter. ESPs help filter these particles, ensuring that harmful emissions are minimized, and regulatory compliance is met.
Fume Mitigation with Electrostatic Precipitators
In industries such as metal smelting, chemical processing, controlling fumes is essential to prevent toxic exposure to workers and the surrounding environment. ESPs are particularly effective in fume mitigation, capturing a wide range of harmful gaseous particles and providing a safer working environment. By using electrostatic attraction, ESPs can trap even the finest particles, preventing their release into the air.
Exhaust Air Treatment with ESPs
Exhaust air treatment is an essential part of managing industrial emissions. ESPs provide an efficient means of removing particulate matter from exhaust gases before they are released into the atmosphere. This is critical not only for meeting environmental regulations but also for maintaining indoor air quality in manufacturing and industrial environments. With increasing environmental awareness and stricter regulations, industries are relying more on ESPs to treat exhaust air and reduce their environmental impact.
Comparison with Other Filtration Technologies
| Technology | Efficiency | Maintenance | Cost | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrostatic Precipitator | 99% for dust removal | Low (vibration/ultrasonic) | Low operational costs | Power plants, cement, steel, chemicals |
| Baghouse Filter | 85-95% | Moderate (filter replacement) | Moderate to High | Cement, steel, power plants |
| Wet Scrubber | 85-90% | High (requires water disposal) | High operational costs | Chemical plants |
Conclusion
Electrostatic precipitators play a critical role in industrial air pollution control, providing a highly efficient, low-maintenance solution for removing particulate matter from exhaust gases. With their ability to capture both coarse and fine particles, ESPs are essential in industries such as power generation, cement production, steel manufacturing, and chemical processing. Moreover, their effectiveness in fume mitigation and exhaust air treatment makes them indispensable for improving air quality and meeting regulatory standards.
FAQ
1. How does an electrostatic precipitator work?
An electrostatic precipitator works by charging the particles in the air with a high-voltage electric field. These charged particles are then attracted to a grounded collector, where they are collected and removed from the air.
2. What industries use electrostatic precipitators?
Electrostatic precipitators are commonly used in power plants, cement manufacturing, steel mills, chemical and petrochemical plants, and mining operations to control particulate emissions.
3. How effective are electrostatic precipitators?
Electrostatic precipitators are highly efficient, capable of removing up to 99% of airborne particulate matter, including fine dust and fume particles.
4. What are the benefits of using an electrostatic precipitator?
Electrostatic precipitators offer high efficiency, low maintenance, energy efficiency, and scalability, making them an ideal solution for industrial air pollution control.
5. How do electrostatic precipitators contribute to fume mitigation?
Electrostatic precipitators are effective in capturing harmful fumes produced in industrial processes by charging and collecting particles from the exhaust gases, ensuring cleaner air and safer working environments.



 English
English Français
Français عربى
عربى 简体中文
简体中文