-
Top 5 Common Problems with Dust Control Systems and How to Fix Them
Dust control systems are integral to maintaining clean air and preventing pollution in various industrial sectors. A well-designed dust control system is essential for minimizing hazardous airborne particles, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations, and improving workp...
-
Bag Filters vs. Cartridge Filters: Which is Better for Your System?
Introduction In industries where air pollution control and waste gas treatment are crucial, selecting the right type of dust filter is essential for both operational efficiency and environmental responsibility. Among the various filtration systems, bag filters and cartridge filte...
-
The Role of Bag Filters in Preventing Air Pollution: Key Benefits and Applications
Introduction Air pollution remains a significant global concern, especially in industrial environments where the emissions of particulate matter, harmful gases, and toxins are frequent. Effective air pollution control systems are crucial to ensuring that industries comply with en...
The Ultimate Choice for Industrial Dust Control? Is the Horizontal Electrostatic Precipitator Truly Omnipotent?
In-Depth Analysis: The Working Principle and Core Advantages of Horizontal Electrostatic Precipitators
In today’s industrial landscape, environmental protection is no longer an optional extra but a lifeline for business survival and growth. Particulate matter emissions from flue gas, as a primary source of industrial pollution, pose a severe threat to the atmosphere and human health. To tackle this challenge, various advanced dust control technologies have emerged. Among the many options, the horizontal electrostatic precipitator (HORIZONTAL ELECTROSTATIC PRECIPITATOR) has become a favored solution for many industries due to its efficient and stable performance. But is it truly the ultimate choice for industrial dust control, capable of handling all conditions as the legends suggest? To answer this question, we must delve into its working principles, applicable conditions, and technological limitations.
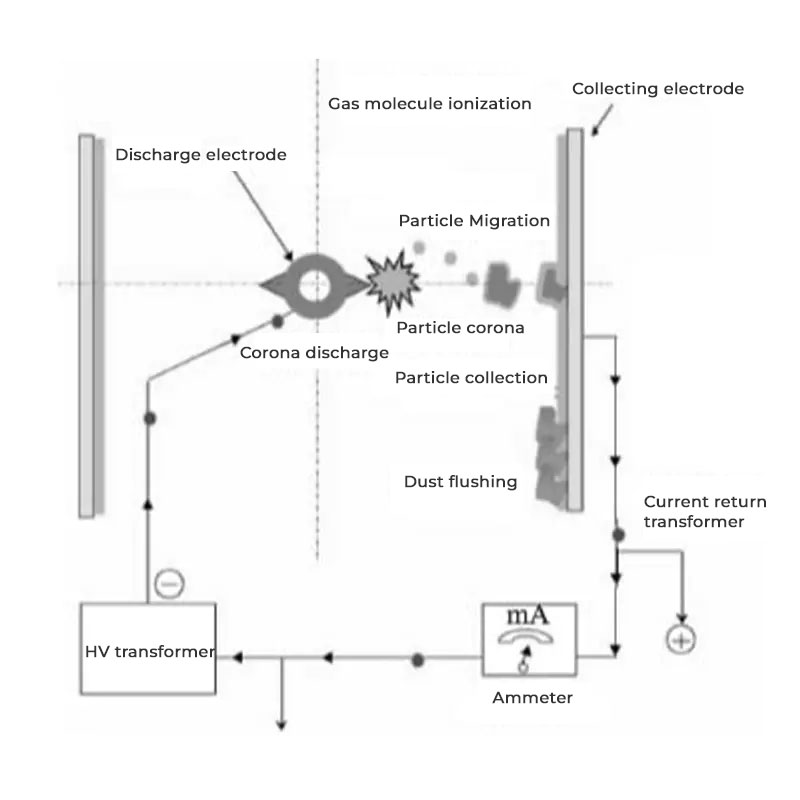
The core principle of a horizontal electrostatic precipitator is to use a high-voltage electric field to charge dust particles in the flue gas and then separate them from the gas stream using electrostatic force. While this process sounds simple, it is underpinned by sophisticated physics and engineering principles.
First, the dust-laden flue gas enters the electrostatic precipitator and passes through a special flow distribution device, ensuring the gas flow is uniform within the electric field area. Subsequently, the flue gas enters the electric field, which is composed of cathodes and anode plates. The cathodes typically have a point-discharge structure, which, under the action of high-voltage direct current, generates a powerful corona discharge. This discharge produces a large number of negative ions and electrons. These particles collide with the dust particles in the flue gas, causing the dust particles to become negatively charged.
Once the dust particles are charged, they swiftly move towards the positively charged anode plates under the influence of the electric field’s Coulomb force. Upon adhering to the anode plates, the dust particles gradually accumulate in layers. To prevent the dust layer from becoming too thick and affecting removal efficiency, the precipitator uses a timed rapping mechanism to dislodge the dust from the anode plates and cathode lines. The dust then falls into hoppers at the bottom and is eventually discharged through an ash conveying system.
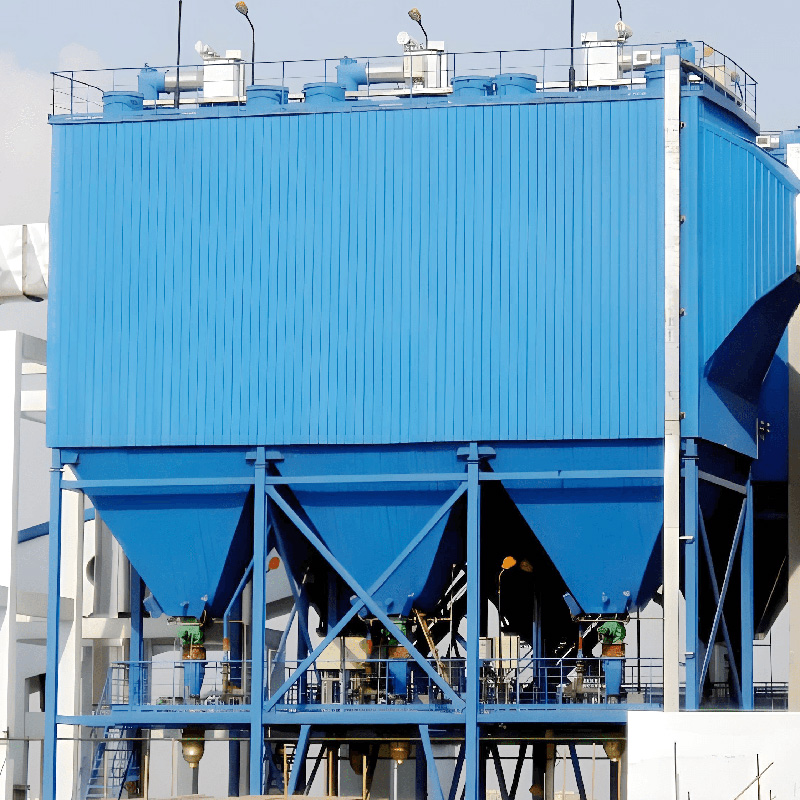
The advantage of a horizontal electrostatic precipitator lies in its unique structural design. The flue gas flows horizontally, while the electric field is perpendicular to the gas flow. This design allows the flue gas to interact thoroughly with the electric field as it passes through multiple electric field sections. By combining multiple electric fields in a series, the dust removal efficiency can be significantly improved. Our company can currently achieve a six-field combination structure, which means the flue gas undergoes six consecutive electrostatic dust removal processes, ensuring that even the smallest particles are effectively captured.
Additionally, horizontal electrostatic precipitators have a natural advantage in handling large volumes of high-temperature flue gas. Their design can accommodate operating temperatures up to 350°C, making them an excellent performer in treating the flue gas from many high-temperature industrial furnaces and kilns. Furthermore, since they do not use consumable filter bags, their operational and maintenance costs are relatively low, and their equipment life is long, making them an ideal choice for many large industrial enterprises.
Key Challenges and Applicable Conditions: Not All Dust Is Easily Managed
Despite the excellent performance of the horizontal electrostatic precipitator, it is not a cure-all solution. Its dust removal efficiency largely depends on the resistivity of the dust in the flue gas. This is a crucial physical parameter that measures the dust’s electrical conductivity. When the dust resistivity is too low, the charged dust particles release their charge immediately upon reaching the anode plate, causing them to bounce back and create secondary dust re-entrainment, which lowers efficiency. Conversely, when the resistivity is too high, the dust particles form an insulating layer on the anode plate, hindering the release of charge. This can lead to an electric field breakdown and a “back corona” phenomenon, which severely affects the equipment’s normal operation.
Therefore, the horizontal electrostatic precipitator has a strict applicable range for dust resistivity, typically requiring it to be within the range of $10^4 \le \rho \le 5 \times 10^{10} \Omega \cdot cm$. For dust that falls outside this range, special pre-treatment measures, such as humidification, temperature adjustment, or the addition of conditioning agents, are necessary to adjust the dust’s resistivity to its optimal working range.
In addition to resistivity, the precipitator’s design must also fully consider the relationship between the wind speed in the electric field section and the depth of the electric field. If the wind speed is too high, the charged dust particles may be carried out of the electric field by the gas flow before they can reach the anode plate, leading to a decrease in dust removal efficiency. Therefore, during the design phase, it is essential to precisely calculate the electric field size and layout based on the flue gas flow rate and dust characteristics, ensuring that the charged particles have enough time and space to migrate to the anode plate. The multi-field series combination structure can effectively extend the residence time of the flue gas in the electric field, thereby overcoming this challenge.
Applicable Scenarios and Performance Metrics: Who Is the Best User for This Technology?
Based on its unique working principle and resistivity requirements, the horizontal electrostatic precipitator plays a pivotal role in specific industries. Its main application areas include:
- Power Industry: Coal-fired power plants are a major market for electrostatic precipitators. The dust resistivity in coal combustion flue gas is often within the optimal working range for electrostatic precipitators, and the high gas volume and temperature are well-suited for treatment by horizontal units. Anhui Tiankang Environmental Technology Co., Ltd has extensive experience in providing customized horizontal electrostatic precipitator solutions to the power industry, helping them achieve strict emission standards efficiently and reliably.
- Iron and Steel Industry: In processes such as sintering, coking, and blast furnaces, the generated flue gas has a high temperature and high dust concentration. With a suitable design, horizontal electrostatic precipitators can effectively treat this complex flue gas, ensuring compliant emissions.
- Cement Industry: The kiln tail gas in cement plants also has characteristics of high temperature and high dust. The horizontal electrostatic precipitator can operate stably and efficiently capture cement dust, making it an indispensable environmental protection device for cement production lines.
In terms of performance metrics, the horizontal electrostatic precipitator performs exceptionally well. It can handle inlet flue gas dust concentrations of up to $<100g/Nm^3$, and after treatment, the outlet dust concentration can generally be reduced to $<30mg/Nm^3$. This emission level meets the environmental regulations of most countries and regions. In certain special applications, through optimized design and operating parameters, the emission concentration can even be brought down to a lower level.
Summary: The Horizontal Electrostatic Precipitator—A Powerful Force with Boundaries
In conclusion, the horizontal electrostatic precipitator is undoubtedly an efficient, stable, and technologically mature dust removal device. It demonstrates unparalleled advantages in treating high-volume, high-temperature flue gas with moderate dust resistivity. However, it is not “omnipotent.” Its dust removal efficiency is constrained by various factors, including dust resistivity, electric field design, and operating parameters.
Therefore, when selecting a dust removal device, businesses must conduct a comprehensive and professional evaluation rather than blindly pursuing the “universality” of a single technology. For specific conditions, such as excessively high or low dust resistivity, or particularly high flue gas humidity, it may be necessary to combine the horizontal electrostatic precipitator with other dust removal technologies (e.g., wet electrostatic precipitators, bag filters, etc.) or implement targeted technical modifications to achieve the best possible dust removal results.
The horizontal electrostatic precipitator is like a “specialist” with unique skills—it can exert extraordinary capabilities within its specific field of expertise. By correctly understanding and applying it, we can truly solve industrial dust control challenges and create a cleaner, healthier production environment for us all.



 English
English Français
Français عربى
عربى 简体中文
简体中文