-
Top 5 Common Problems with Dust Control Systems and How to Fix Them
Dust control systems are integral to maintaining clean air and preventing pollution in various industrial sectors. A well-designed dust control system is essential for minimizing h...
-
Bag Filters vs. Cartridge Filters: Which is Better for Your System?
Introduction In industries where air pollution control and waste gas treatment are crucial, selecting the right type of dust filter is essential for both operational efficiency and...
-
The Role of Bag Filters in Preventing Air Pollution: Key Benefits and Applications
Introduction Air pollution remains a significant global concern, especially in industrial environments where the emissions of particulate matter, harmful gases, and toxins are freq...
-
A Step-by-Step Guide to Maintaining Your Electrostatic Precipitator
An electrostatic precipitator (ESP) is a crucial component in industrial processes that need to control particulate pollution, particularly in power plants, cement factories, and o...
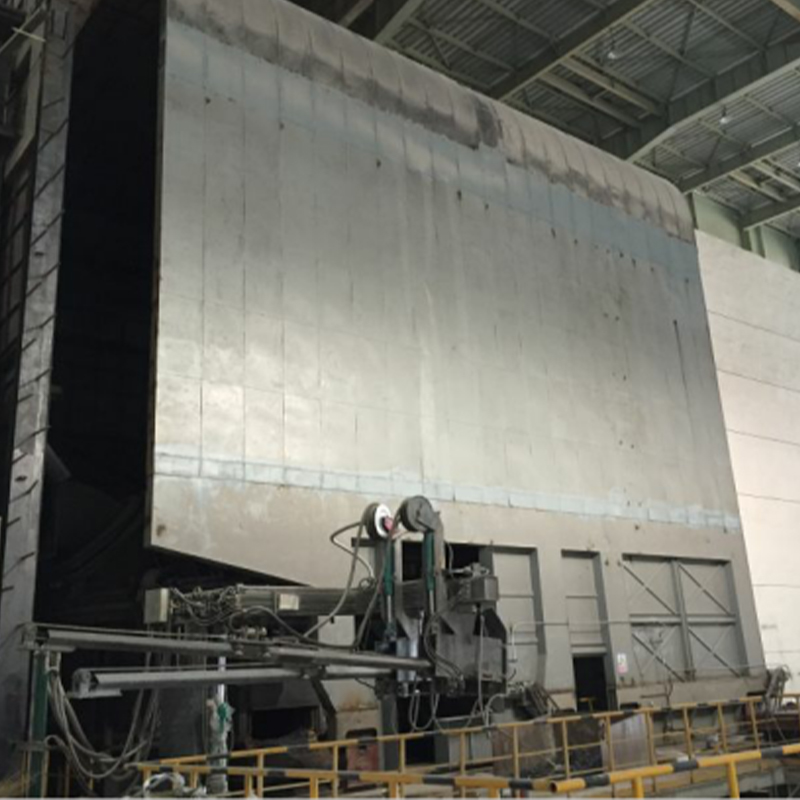
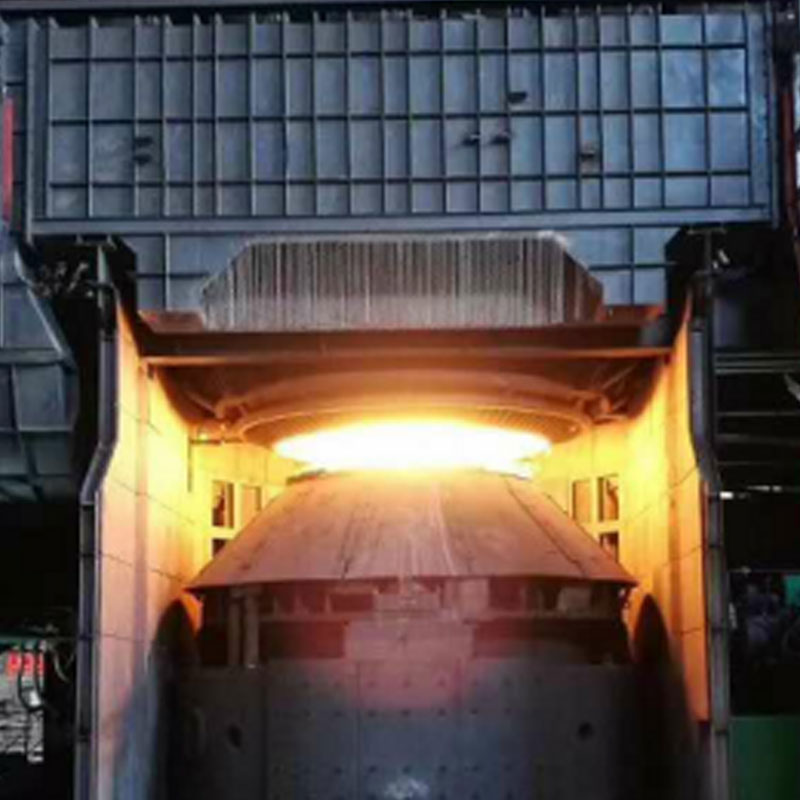
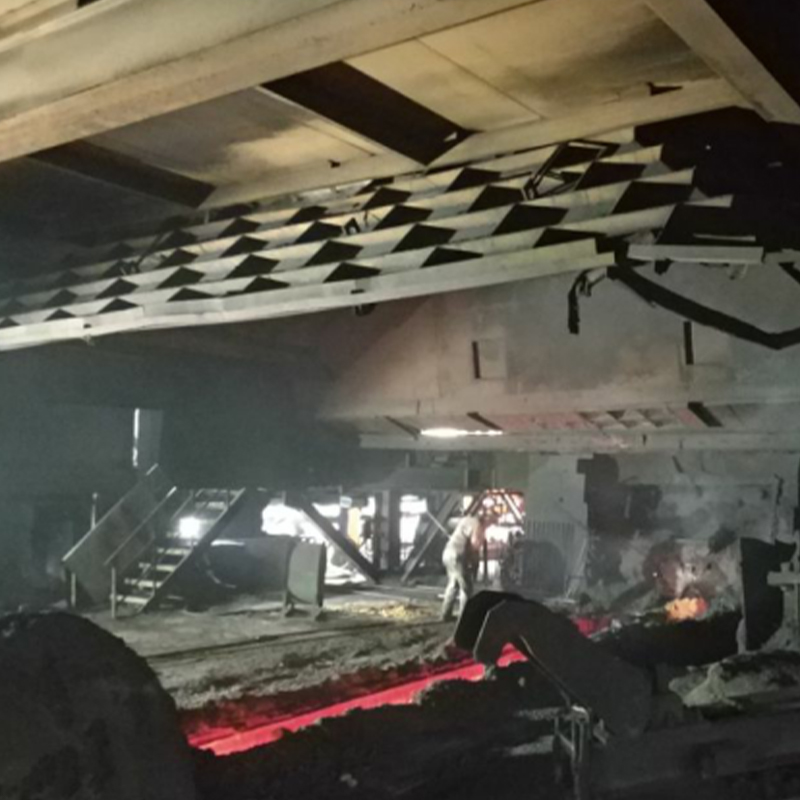
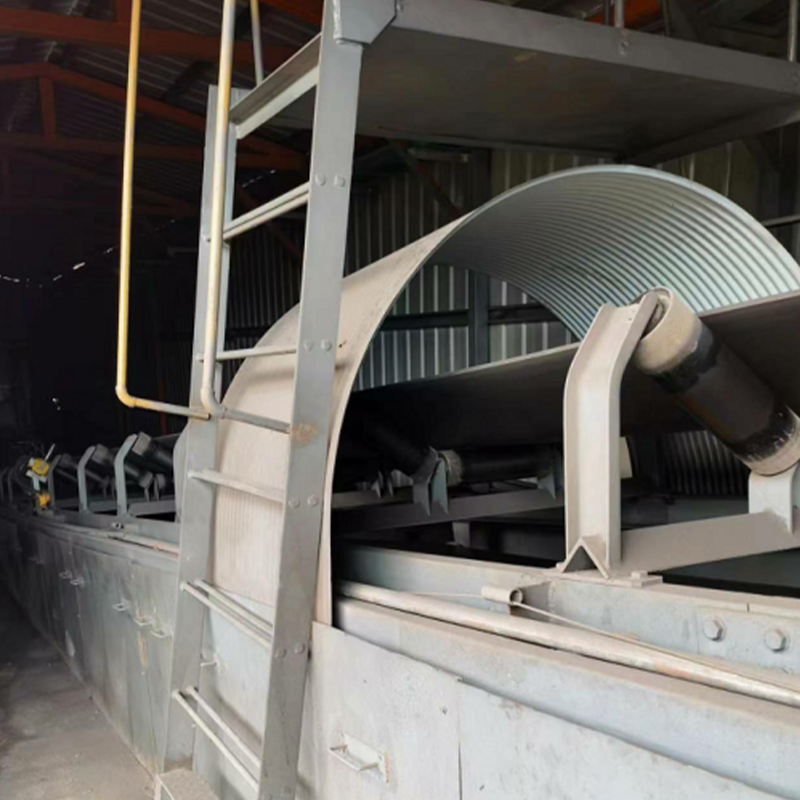
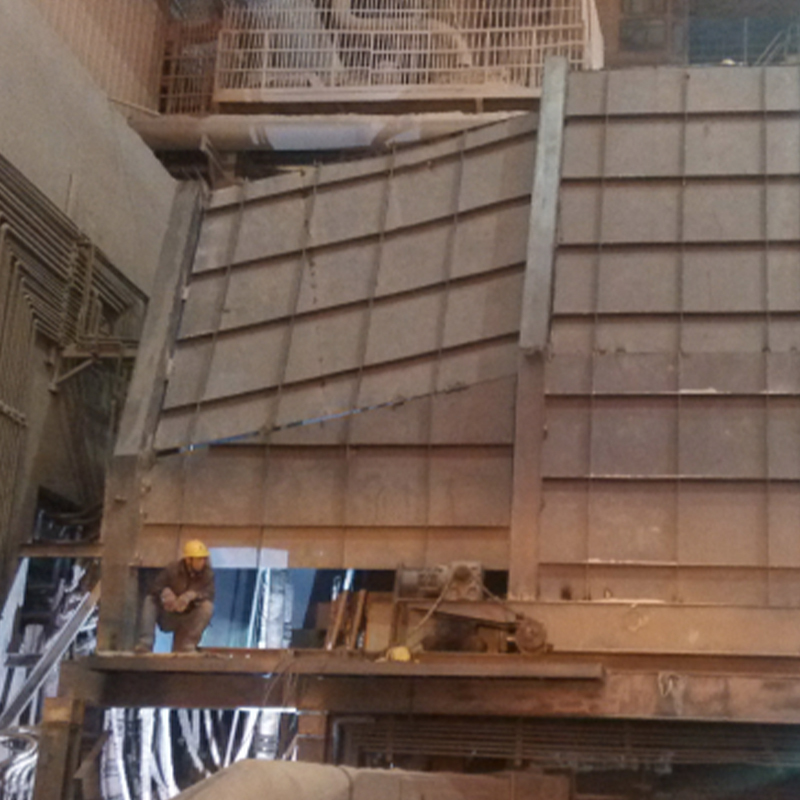
Industrial Dust Collection Hoods Contractor
There are many types of collection hoods. Different collection hoods are designed according to different working conditions and different dust generating points. Commonly used collection hood types include fixed hoods, mobile hoods and rotating hoods. Its main function is to collect the smoke generated by the dust generating point into the collection hood as soon as possible to prevent it from overflowing and spreading.

Anhui Tiankang Environmental Technology Co., Ltd. (formerly Wuxi Mingtian Environmental Protection Equipment Co., Ltd.) was established in 2002. It is a private high-tech enterprise dedicated to environmental protection and governance. The company is mainly engaged in environmental engineering design, environmental protection facility operation and environmental pollution control technology research and development, and undertakes various dust removal systems, flue gas desulfurization and denitrification systems and VOC systems and other engineering general contracting business. We are Customized Industrial Dust Collection Hoods Factory and China Industrial Dust Collection Hoods Contractor, At present, the company's products include various bag dust collector systems (including raw materials, batching, pelletizing, sintering, ironmaking, steelmaking, rolling and other aspects of steel mills; foundry industry, pharmaceutical industry, glass industry, cement industry, non-ferrous metal smelting industry, etc.), converter primary dust removal flue gas recovery system, slag treatment system, VOC treatment system (including activated carbon adsorption device, catalytic combustion device, RTO and UV pretreatment + zeolite wheel adsorption + RCO device, etc.), as well as flue gas heat exchanger, cooler, capture hood (including electric furnace fully enclosed hood, roof hood, converter front and rear hood, blast furnace tapping port, slag skimmer hood, various belt hoods, and various scattered point hoods in steelmaking workshop, etc.), mobile ventilation slots, mufflers, desulfurization towers, ash conveying equipment, ventilation duct flexible compensators, pipeline sliding supports, condensate drainers, bags, keels and other customized accessories.
Tiankang Environment has two branches. One is Wuxi Mingtian Environmental Protection Equipment Co., Ltd., which is located in Wuxi, a famous city in the south of the Yangtze River with a developed economy and picturesque scenery. It has convenient transportation and rich natural and cultural landscapes. The other is Anhui Tiankang Environmental Technology Co., Ltd. (formerly Anhui Mingtian Energy Saving and Environmental Protection Engineering Co., Ltd.), which is located in Lu'an, an old revolutionary base with a long history, mountains and water, and a pleasant climate. The company sincerely welcomes friends from all walks of life to visit and guide with an open attitude. It is willing to provide technical services for all walks of life and provide a stage for people with lofty ideals to display their wisdom and talents.
The company focuses on the future, is determined to protect the environment, and regards returning a fresh, blue and clear sky to mankind as the company's goal!
How do industrial FES fume extraction systems compare to traditional ventilation methods?
Industrial air quality management is critical for worker safety, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency. Two primary approaches dominate this field: traditional ventilation methods (e.g., general dilution ventilation, local exhaust systems) and advanced industrial FES (Fume Extraction Systems).
1. Understanding Traditional Ventilation Methods
Traditional ventilation relies on broad airflow management, including:
- Dilution Ventilation: Mixes contaminated air with fresh air to reduce pollutant concentrations.
- Local Exhaust Ventilation (LEV): Uses hoods and ducts to capture contaminants at the source.
While these methods are widely implemented, they often suffer from inefficiencies, such as high energy consumption, incomplete pollutant capture, and difficulty handling high-toxicity or high-volume emissions.
2. Industrial FES Fume Extraction Systems: Core Principles
Industrial FES fume extraction systems represent a technological evolution, combining targeted capture with advanced filtration. Key components include:
- High-efficiency dust collection hoods (fixed, mobile, or rotating) designed for specific emission points.
- Adaptive airflow control to optimize suction based on real-time demand.
- Integrated filtration technologies (e.g., bag filters, activated carbon adsorption, catalytic oxidation).
Unlike traditional systems, FES solutions prioritize source capture, minimizing pollutant dispersion while reducing energy waste.
3. Comparative Analysis: FES vs. Traditional Ventilation
3.1 Capture Efficiency
- FES Systems: Utilize precisely engineered dust collection hoods to enclose emission points (e.g., electric furnace hoods, converter hoods, tapping port hoods), achieving >95% capture rates.
- Traditional LEV: Often struggles with fugitive emissions due to inadequate hood design or airflow imbalances.
3.2 Energy and Operational Costs
- FES Systems: Use variable-frequency drives (VFDs) and demand-based extraction, cutting energy use by 30–50% compared to constant-volume traditional systems.
- Dilution Ventilation: Requires excessive airflow to meet safety thresholds, increasing HVAC loads.
3.3 Flexibility and Adaptability
- FES Systems: Modular designs allow customization for industries like steelmaking (sintering, pelletizing), pharmaceuticals, or cement.
- Traditional Methods: Rigid ductwork and static hoods limit reconfiguration for new processes.
3.4 Compliance and Environmental Impact
Modern industrial FES fume extraction systems integrate end-of-line treatments (e.g., RTO, SCR denitrification) to meet stringent emissions standards, whereas traditional systems often require retrofits.
4. Industry Applications and Case Examples
- Steel Industry: Converter primary dust removal systems in FES setups outperform traditional scrubbers in particulate recovery.
- Foundries: Enclosed hoods with FES reduce silica exposure more effectively than canopy hoods.
- Pharmaceuticals: VOC abatement via FES (e.g., zeolite rotor + RCO) ensures solvent recovery without secondary pollution.
5. Technological Integration and Future Trends
Emerging advancements in industrial FES fume extraction systems include:
- IoT-enabled monitoring for predictive maintenance.
- Hybrid filtration (e.g., electrostatic precipitators + baghouses).
- Low-noise mufflers and heat recovery from extracted fumes.
Industrial FES fume extraction systems offer superior efficiency, cost savings, and scalability compared to traditional ventilation. By leveraging precision-engineered dust collection hoods and smart airflow management, they address the limitations of older methods while aligning with global sustainability goals. For industries seeking compliance and long-term operational benefits, transitioning to FES technology is a strategic imperative.
How effective are dust collection hoods in capturing fine particulate matter?
Dust collection hoods are critical components in industrial air pollution control systems, designed to capture and contain fine particulate matter (PM) at emission sources before it disperses into the workplace or environment. Their effectiveness depends on factors such as design, placement, airflow dynamics, and the nature of the dust source. Industries such as steel manufacturing, cement production, pharmaceuticals, and metal smelting rely on these systems to maintain air quality and comply with environmental regulations.
Anhui Tiankang Environmental Technology Co., Ltd, as a high-tech enterprise specializing in environmental protection solutions, emphasizes the importance of tailored dust collection hood designs for different industrial applications. Their expertise in dust removal systems, including various hood types such as fixed, mobile, and rotating hoods, highlights the necessity of optimizing capture efficiency based on specific working conditions.
The Role of Dust Collection Hoods in Industrial Ventilation
Dust collection hoods serve as the first line of defense in industrial ventilation systems by capturing airborne particles at their source. Their primary function is to contain and direct contaminated air into ductwork, where it can be filtered or treated before release. The efficiency of a hood depends on its ability to generate sufficient airflow to overcome particle dispersion forces, such as thermal buoyancy or mechanical agitation.
Different hood designs are employed based on the dust generation mechanism. Enclosed hoods, for example, are used in high-emission processes like electric arc furnace operations, where fugitive dust must be fully contained. Partial hoods, such as canopy or side-draft hoods, are used when full enclosure is impractical, relying on strategic placement and airflow control to capture emissions. The selection of the appropriate hood type directly impacts particulate capture rates.
Factors Influencing the Capture Efficiency of Dust Collection Hoods
The effectiveness of dust collection hoods in capturing fine particulate matter is influenced by several key factors:
- Hood Design and Geometry – The shape and size of the hood must align with the emission source. A well-designed hood ensures optimal airflow patterns, minimizing particle escape. For instance, flanged hoods reduce air entrainment from surrounding areas, improving capture efficiency.
- Airflow Velocity and Volume – Sufficient airflow is required to overcome particle inertia and draw contaminants into the hood. However, excessive velocity can lead to energy waste, while insufficient velocity allows particle escape.
- Placement Relative to the Emission Source – Proximity and orientation significantly affect capture efficiency. Hoods placed too far from the source or at incorrect angles may fail to contain dust effectively.
- Dust Particle Characteristics – Fine particulate matter behaves differently than coarse dust, often remaining suspended longer. Hoods must account for particle size, density, and electrostatic properties.
- Process Variability – Some industrial processes, such as steelmaking or material handling, generate intermittent or fluctuating dust emissions. Adjustable or mobile hoods may be necessary to adapt to changing conditions.
Common Types of Dust Collection Hoods and Their Applications
Different industrial processes require specialized hood designs to maximize particulate capture. The following table summarizes common hood types and their typical applications:
| Hood Type | Description | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Fixed Hoods | Permanently installed, often enclosing dust sources completely or partially. | Steelmaking (tapping stations, converters), cement kilns, pharmaceutical mixing. |
| Mobile Hoods | Adjustable or movable to accommodate changing emission points. | Welding operations, material transfer points, maintenance activities. |
| Rotating Hoods | Designed to follow moving or rotating emission sources. | Ladle metallurgy, rotary kilns, conveyor belt transfer points. |
| Canopy Hoods | Overhead capture, relying on thermal or buoyant airflow. | Furnace operations, drying processes, paint booths. |
| Side-Draft Hoods | Lateral capture, often used when overhead access is restricted. | Grinding, sanding, machining operations. |
Each hood type has distinct advantages depending on the dust generation mechanism. For example, fully enclosed hoods in steelmaking prevent fugitive emissions during tapping, while mobile hoods in welding operations allow flexibility in capturing intermittent fumes.
Challenges in Capturing Fine Particulate Matter
Despite advancements in hood design, capturing fine particulate matter remains challenging due to its tendency to remain airborne and disperse easily. Key challenges include:
- Aerodynamic Behavior – Fine particles (PM2.5 and smaller) follow air currents rather than settling, requiring precise airflow control.
- Process Interference – Some industrial operations, such as material dumping or pneumatic conveying, generate sudden bursts of dust that may overwhelm static hoods.
- Worker Accessibility – Enclosed hoods may hinder operational efficiency, leading to compromises in design that reduce capture effectiveness.
- Maintenance and Wear – Accumulated dust on hood surfaces can disrupt airflow, reducing efficiency over time.
To mitigate these challenges, modern dust collection systems integrate real-time airflow monitoring, automated hood adjustments, and secondary filtration to ensure consistent performance.
Industry-Specific Considerations
Different industries face unique dust control requirements, necessitating customized hood solutions:
- Steel Industry – Processes like sintering, blast furnace tapping, and converter operations generate heavy dust loads, requiring robust, high-capacity hoods with heat resistance.
- Cement and Glass Manufacturing – High-temperature emissions and abrasive dust necessitate durable hood materials and efficient cooling mechanisms.
- Pharmaceuticals – Hygienic, easy-to-clean hood designs are critical to prevent cross-contamination.
- Non-Ferrous Metal Smelting – Toxic fumes demand tightly sealed hoods with secondary filtration to prevent worker exposure.
Anhui Tiankang Environmental Technology Co., Ltd’s experience in these sectors underscores the importance of industry-specific engineering in dust hood design. Their solutions incorporate patented technologies to enhance capture efficiency while maintaining operational flexibility.
Technological Advancements and Future Trends
Innovations in dust collection hood technology focus on improving energy efficiency, adaptability, and smart monitoring. Emerging trends include:
- Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Modeling – Used to simulate airflow and optimize hood placement before installation.
- Self-Adjusting Hoods – Automated systems that modify airflow based on real-time dust emission levels.
- Low-Energy Designs – Hoods that maximize capture efficiency while minimizing power consumption.
- Integrated Filtration – Combining hoods with advanced filtration media to enhance fine particulate retention.
These advancements aim to address both environmental regulations and operational efficiency, ensuring dust collection systems remain effective in increasingly stringent regulatory landscapes.
Dust collection hoods play a vital role in controlling fine particulate matter across industrial applications. Their effectiveness depends on proper design, placement, and maintenance, with industry-specific considerations ensuring optimal performance. While challenges such as fine particle dispersion and process variability persist, technological advancements continue to improve capture efficiency. Companies specializing in environmental engineering, such as Anhui Tiankang Environmental Technology Co., Ltd, contribute to these improvements through tailored solutions and innovative designs. As industries evolve, dust collection hoods will remain a cornerstone of air pollution control, safeguarding both worker health and environmental compliance.



 English
English Français
Français عربى
عربى 简体中文
简体中文