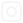
How Can Dust Filters Help in Flue Gas Treatment and Emission Control?
 By Admin
By Admin
Introduction
The global industrial landscape, particularly in metallurgy, has been undergoing significant shifts due to stricter environmental regulations and increased concerns over pollution. As a result, the importance of air quality and the reduction of harmful emissions has never been more prominent. Dust filters, crucial in this context, play an essential role in improving air quality, reducing harmful pollutants, and ensuring compliance with environmental standards. The use of dust filters spans a wide range of industries, including steel manufacturing, non-ferrous metal smelting, and waste gas treatment.
Understanding Dust Filters: Basics and Functionality
Dust filters, as the name implies, are designed to trap dust particles and prevent them from entering the air. These filters come in various types, such as bag filters, electrostatic precipitators, and cyclone separators. Each type operates based on different principles, allowing for versatility in their applications across different industries.
Types of Dust Filters
- Bag Filters: These are designed to capture dust particles as air passes through a fabric filter. They are widely used in industries where particulate emissions are significant, such as steelmaking and cement production.
- Electrostatic Precipitators: These filters use electric fields to charge particles, causing them to be attracted to a collection surface. They are especially effective for fine dust and gases in non-ferrous metal industries.
- Cyclone Separators: Using centrifugal force, cyclone separators remove larger particles from the air stream. These are typically used as pre-filters before other filtration systems.
How Dust Filters Work
Dust filters primarily rely on physical and electrostatic principles to capture particulate matter. As air flows through the filter medium, particles of various sizes are either trapped on the surface or attracted to charged electrodes. The efficiency of these systems is crucial in ensuring that emissions are kept to a minimum.
Comparison of Dust Filter Types
| Filter Type | Working Principle | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|
| Bag Filter | Air passes through fabric, trapping particles | Steel mills, cement plants |
| Electrostatic Precipitator | Uses electric charge to attract particles | Non-ferrous metal smelting, copper |
| Cyclone Separator | Centrifugal force separates larger particles | Pre-filtering applications in smelting |
Application of Dust Filters in Metallurgy
The metallurgy industry generates a variety of particulate matter during metal extraction and processing. Dust filters are essential for controlling emissions and maintaining air quality in these settings. Below are the applications of dust filters in several metallurgical processes.
Dust Filters in Steelmaking
Steel production is known for its high dust emissions, which can include slag, metal oxide particles, and other combustion residues. Dust filters in steel mills help capture these particles, improving air quality and ensuring the factory complies with environmental standards. The dust collected can sometimes be reprocessed, adding a level of resource recovery to the operation.
- Challenges: Steel production involves extremely high temperatures and harsh conditions, making the filtration process more difficult. Bag filters are commonly used to handle the large volume of particulate matter generated during the process.
Dust Filters in Non-Ferrous Metal Smelting
Non-ferrous metals such as copper, aluminum, zinc, and lead are processed through various smelting methods, often generating toxic dust and fumes. Dust filters play an essential role in reducing the emission of these hazardous particles, protecting both the environment and workers. Electrostatic precipitators are often used in these settings, given their ability to capture fine particles effectively.
- Challenges: The high temperatures and corrosive nature of some fumes require filters that are durable and able to withstand extreme conditions. In copper and aluminum smelting, the particles can be highly reactive, requiring more advanced filtration technologies.
Dust Filter Applications in Different Metallurgical Industries
| Metallurgical Process | Emissions | Filter Type | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steelmaking | Slag, metal oxide dust, combustion residues | Bag Filter | High temperature, large volume of dust |
| Copper Smelting | Copper oxide, sulfuric acid fumes | Electrostatic Precipitator | High temperature, corrosive particles |
| Aluminum Smelting | Aluminum oxide, toxic fumes | Electrostatic Precipitator | Corrosive, reactive materials |
| Zinc and Lead Smelting | Zinc oxide, lead particles | Electrostatic Precipitator | Toxic, fine particulate matter |
Dust Filters in Waste Gas Treatment and Emission Control
In industries such as metallurgy, chemical processing, and power generation, managing waste gas and emissions is a key challenge. Dust filters contribute significantly to improving the efficiency of waste gas treatment systems. These systems not only capture particulate matter but also help in treating and controlling gases such as sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and nitrogen oxides (NOx).
Flue Gas Treatment
Flue gas, produced from combustion processes in industries such as steelmaking and power generation, contains a mixture of harmful gases and particulate matter. Dust filters are essential in the treatment of these gases, as they capture particulates and, in some cases, assist in reducing the amount of harmful gases emitted.
Emission Control
Emission control systems utilize a variety of filtration methods to capture particulates and gases before they are released into the atmosphere. In industries like cement and chemical production, where harmful particles are generated, dust filters are integrated into the exhaust systems to ensure compliance with local air quality standards.
Challenges: The complexity of emission control lies in managing both particulate matter and gaseous pollutants. While dust filters excel at particulate capture, additional technologies such as scrubbing and catalytic reduction may be required to manage gases.
Waste Gas Recovery
Waste gas recovery systems are designed to capture and reuse gases that would otherwise be emitted into the atmosphere. Dust filters play a crucial role in removing particulates from waste gas streams before the gas is either released or recycled. In some cases, recovered gases can be used for energy generation, contributing to overall sustainability efforts.
Dust Filter Effectiveness in Waste Gas Treatment
| Waste Gas Type | Pollutants | Filter Type | Efficiency in Emission Control |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flue Gas | Particulate matter, SO₂ | Bag Filter, Cyclone Separator | High efficiency in particulate capture |
| Emission Control | CO₂, NOx, Sulfur compounds | Electrostatic Precipitator | Helps reduce particulate emissions |
| Waste Gas Recovery | Particulate matter, volatile compounds | Bag Filter, Cyclone Separator | Effective in particulates removal, improving gas quality |
Maintenance and Care of Dust Filters
While dust filters play a crucial role in reducing air pollution and improving environmental health, their maintenance is equally important to ensure efficiency. Regular maintenance is necessary to prolong the life of dust filters and ensure their continued performance.
Routine Maintenance Practices
Dust filters require periodic cleaning, especially in industrial applications where high levels of dust are generated. Depending on the filter type, cleaning may involve shaking, pulse-jet cleaning, or backwashing. The type of cleaning method depends on the filter’s design and the nature of the dust it handles.
Replacement and Repair
Filters should be replaced periodically to prevent clogging and maintain efficient airflow. In some cases, components such as the filter bags or electrostatic plates may need repair or replacement to prevent system breakdowns.
Energy Efficiency Considerations
Regular cleaning and maintenance not only prolong the life of dust filters but also improve energy efficiency by preventing pressure drop. This is particularly important in high-energy-consuming applications such as smelting and cement production.
Maintenance Considerations for Dust Filters
| Maintenance Task | Filter Type | Frequency | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cleaning | Bag Filter, Cyclone Separator | Regular intervals (monthly) | Prevent clogging, maintain efficiency |
| Replacement | All Types | Periodic (depends on use) | Ensure proper filter material and fit |
| Inspection | Electrostatic Precipitator | Quarterly | Check for electrode wear and discharge efficiency |
Conclusion
Dust filters play a critical role in controlling particulate emissions and ensuring cleaner air in various industrial sectors, particularly metallurgy and waste gas treatment. As industries continue to face stricter environmental standards, the importance of efficient dust filtration systems will only grow.
FAQ
1. How do I choose the right dust filter for my industry?
Choosing the right dust filter depends on several factors, including the type of dust produced, the temperature and humidity of the environment, and regulatory requirements.
2. How often should dust filters be maintained?
Maintenance frequency varies depending on the type of filter and its usage, but generally, filters should be cleaned monthly and replaced periodically.
3. Can dust filters be recycled?
Some components of dust filters, such as the bags and certain materials, can be recycled, contributing to sustainability.
4. What are the energy implications of dust filter use?
Proper maintenance of dust filters can reduce energy consumption by preventing airflow resistance and pressure drops, ultimately improving system efficiency.
5. How can I ensure compliance with local environmental standards using dust filters?
By selecting filters that meet regulatory standards and performing regular maintenance, you can ensure that your filtration systems are compliant with local emission control laws.



 English
English Français
Français عربى
عربى 简体中文
简体中文